About Upper GI Endoscopy
All You Need to Know About Upper GI Endoscopy
What is an Upper GI Endoscopy?
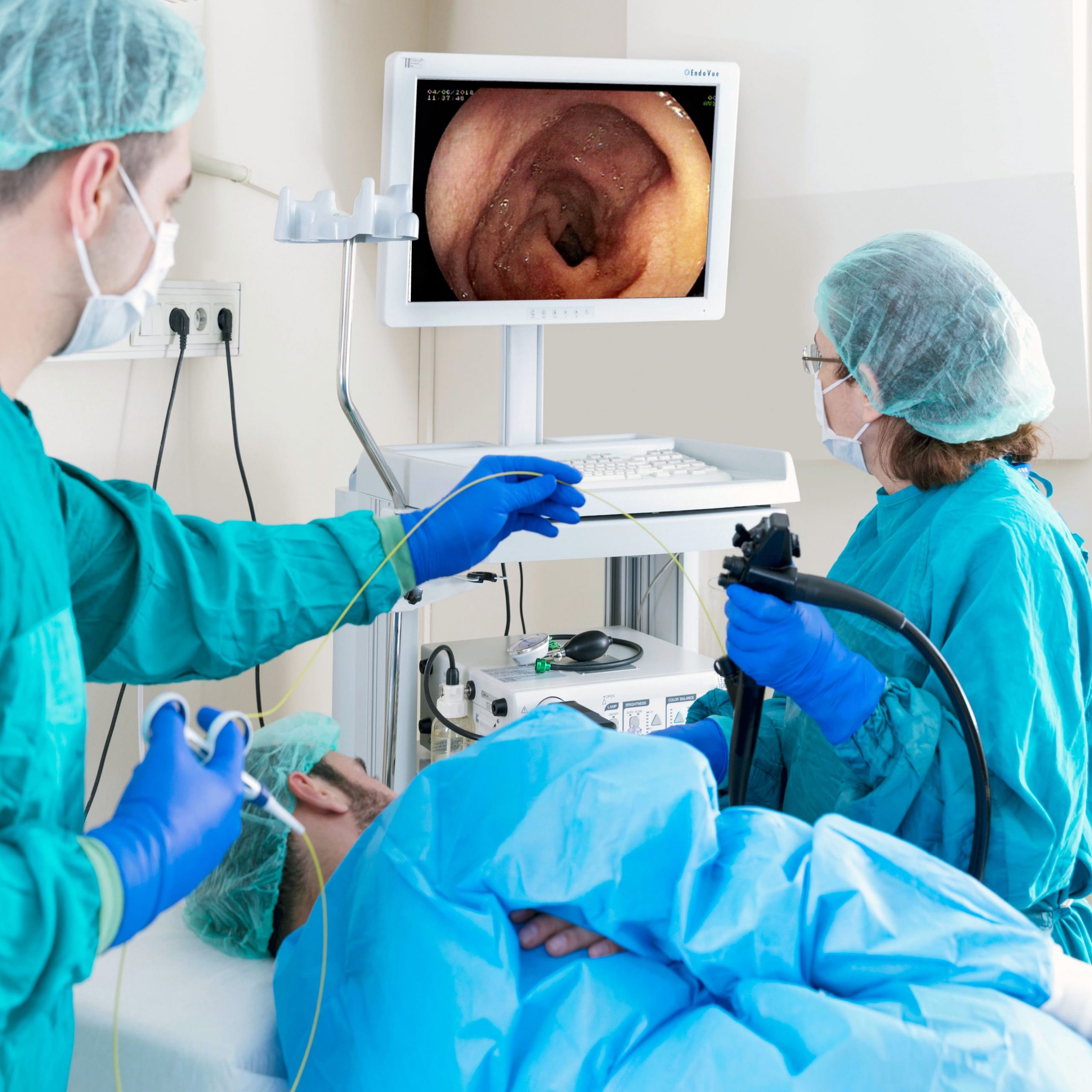
An Upper GI Endoscopy, or esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that allows doctors to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). It involves the use of a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light called an endoscope, inserted through the mouth.
Why is an Upper GI Endoscopy Done?
Doctors recommend this procedure for various reasons, including:
- Diagnosis of Symptoms: To evaluate persistent symptoms such as heartburn, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or difficulty swallowing.
- Detecting Conditions: Identifying issues like ulcers, inflammation, infections, or tumors.
- Monitoring: Checking for progress in conditions like Barrett’s esophagus or gastritis.
- Treatment: Removing polyps, dilating narrowed areas, or stopping bleeding.
Preparation for the Procedure
Proper preparation is essential for a successful endoscopy. Here’s what to expect:
- Fasting: Avoid food and drink for 6–8 hours before the procedure.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any medications or supplements you're taking. You may need to adjust them before the test.
- Consent: Sign a consent form acknowledging that you understand the risks and benefits.
The Procedure Step-by-Step
- Sedation: You may receive a sedative or anesthetic to help you relax.
- Insertion of Endoscope: The doctor inserts the endoscope through your mouth and guides it down the esophagus.
- Visualization: The camera provides a real-time view of the GI tract on a monitor.
- Tissue Samples: If necessary, small tissue samples (biopsies) may be taken for further analysis.
- Duration: The entire procedure typically takes about 15–30 minutes.
What to Expect After the Procedure
- Recovery Time: You'll rest until the sedative wears off, usually about an hour.
- Minor Discomfort: You might experience a sore throat or mild bloating, which resolves quickly.
- Results: Your doctor will discuss the findings and next steps, if any. Biopsy results may take a few days.
Are There Any Risks?
While Upper GI Endoscopy is generally safe, there are some potential risks, including:
- Bleeding (especially if a biopsy is taken).
- Perforation of the digestive tract (rare).
- Adverse reactions to sedatives.
Always discuss the risks with your doctor to understand how they apply to your case.
Benefits of an Upper GI Endoscopy
- Accurate Diagnosis: Offers detailed imaging and the ability to take biopsies.
- Minimally Invasive: No large incisions are needed.
- Quick Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities the same day.
Who Should Consider This Procedure?
Anyone experiencing persistent gastrointestinal symptoms or requiring monitoring for existing conditions should consult their doctor about the need for an Upper GI Endoscopy.
Final Thoughts
An Upper GI Endoscopy is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating conditions of the upper digestive tract. Proper preparation and understanding the procedure can ease any apprehension. If you're experiencing troubling digestive symptoms, don’t hesitate to discuss this option with your healthcare provider.

Share This News