Celiac Disease Symptoms and Treatment
Celiac Disease: Symptoms and Treatment
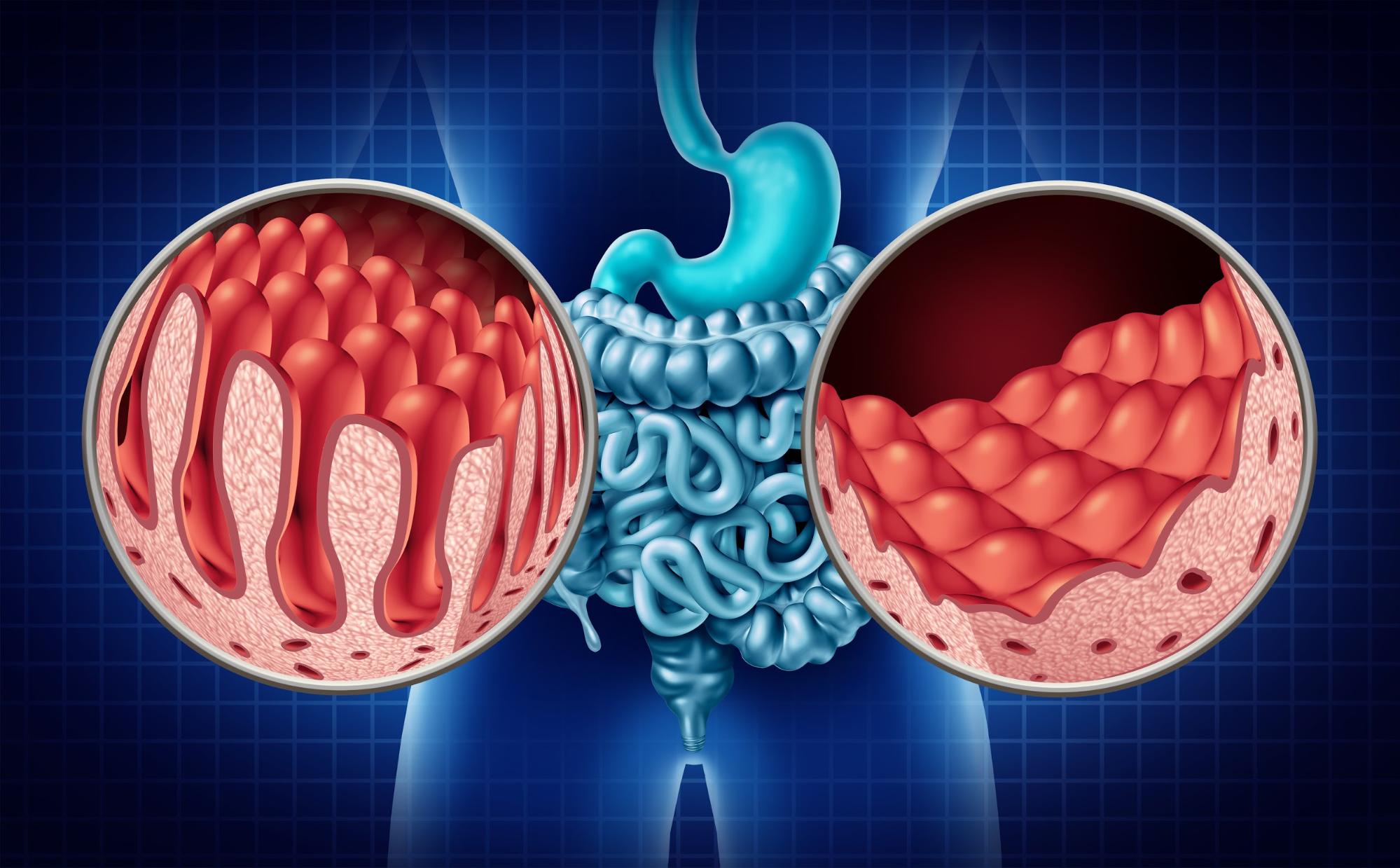
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system reacts abnormally to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This reaction damages the lining of the small intestine, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and various health complications. It can affect people of all ages and is triggered by consuming foods or products containing gluten.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease symptoms can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe. They can also differ between children and adults.
Common Symptoms in Adults:
- Digestive Issues: Diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, bloating, and gas.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite a normal or increased appetite.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness and low energy levels.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Iron-deficiency anemia, due to malabsorption of nutrients.
- Skin Rash: An itchy, blistering skin condition called dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Bone and Joint Pain: Caused by calcium and vitamin D deficiencies.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, numbness, tingling, and even depression or anxiety.
Common Symptoms in Children:
- Growth Problems: Failure to thrive, delayed puberty, or short stature.
- Behavioral Changes: Irritability, mood swings, or difficulty concentrating.
- Frequent Stomach Issues: Chronic diarrhea, vomiting, or bloating.
How is Celiac Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing celiac disease involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and tests:
- Blood Tests: To check for antibodies such as tissue transglutaminase (tTG-IgA).
- Endoscopy: A biopsy of the small intestine to detect damage to the intestinal lining.
- Genetic Testing: To identify genes (HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8) associated with the condition.
It's crucial not to start a gluten-free diet before testing, as this can interfere with accurate results.
Treatment for Celiac Disease
There is no cure for celiac disease, but it can be effectively managed with dietary changes.
Gluten-Free Diet
The cornerstone of treatment is a strict gluten-free diet, which helps:
- Alleviate symptoms.
- Heal the intestinal lining.
- Prevent future complications.
Foods to Avoid:
- Wheat-Based Products: Bread, pasta, cakes, and cookies.
- Barley and Rye: Found in beer, malt, and some processed foods.
- Cross-Contaminated Foods: Items processed in facilities that also handle gluten-containing products.
Foods You Can Enjoy:
- Naturally Gluten-Free Foods: Fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, eggs, dairy, and nuts.
- Gluten-Free Grains: Rice, quinoa, buckwheat, and millet.
Supplements:
Individuals with nutritional deficiencies may require supplements for:
- Iron and Folate: To address anemia.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: To strengthen bones.
- Vitamin B12: To manage neurological symptoms.
Regular Monitoring:
Routine follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to ensure compliance with the diet and to monitor for complications.
Complications if Untreated
Without treatment, celiac disease can lead to severe health issues, such as:
- Osteoporosis: Due to poor calcium absorption.
- Infertility: In both men and women.
- Neurological Disorders: Seizures, migraines, or neuropathy.
- Increased Risk of Other Autoimmune Diseases: Such as type 1 diabetes or thyroid disorders.
Living Well with Celiac Disease
Adopting a gluten-free lifestyle may feel overwhelming initially, but with time, it becomes manageable. Here are some tips:
- Read Labels: Always check for hidden gluten in sauces, dressings, and processed foods.
- Gluten-Free Restaurants: Research dining options with gluten-free menus.
- Join Support Groups: Connect with others to share experiences and tips.
- Educate Friends and Family: Help them understand your dietary needs to avoid accidental exposure.
Final Thoughts
Celiac disease is a life-long condition, but with proper management through a gluten-free diet, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. If you suspect you or a loved one might have celiac disease, consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.

Share This News